Reverse200-1
Hightlighted techniques
- ghidralib for semi-automatic string extraction
Learning the game
We are presented with a file called Reverse. I run the file command against it:
Reverse200-1: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=ee89e6f8d8bc723c2eabc56f150f344af85be5f3, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
it seems to be an ELF file, so I’ll be running it with my docker debian container.
1
2
## ./Reverse200-1
Obfuscated Flag (Hex): 73 0b 22 21 1e 1c 11 22 21 73
seems to print the obfuscated flag
Playing the game
I opened the file in ghidra and modified it a bit to make it more readable
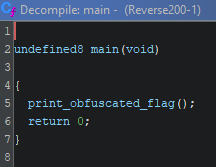
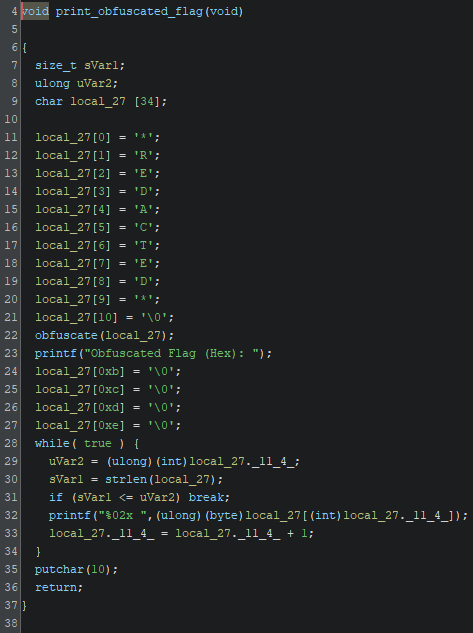
The actual flag seems to be redacted but there’s a call to a obfuscate() function and then every byte of the string is being printed in hex
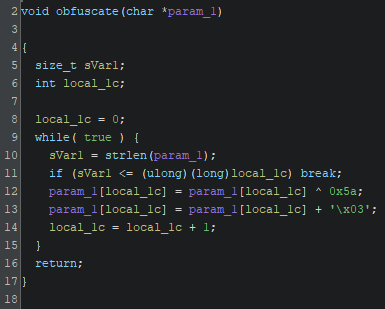
This is the code of the obfuscate() function:
There’s also a deobfuscate() function, but it seems to not do anything
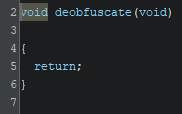
Reading the assembly for this function we can see that it is simply building a string in a variable and then not using it for anything, that’s why the decompiler is not producing any code
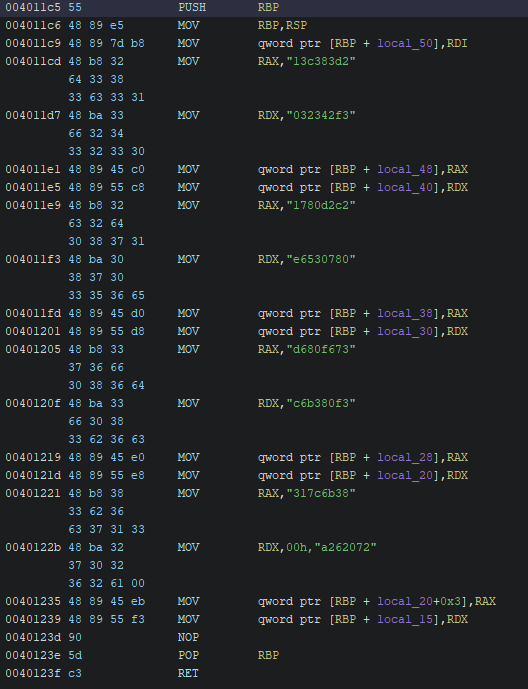
Let’s first create the reversed obfuscate function and then come back to what the flag is. The obfuscate() function seems to simply do a xor and add a constant to the result, so we just reverse that by subtracting the same constant and performing the same xor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def main():
encoded_flag = ""
decoded_flag = ""
for char_i in range(0, len(encoded_flag), 2):
try:
current_char = encoded_flag[char_i: char_i + 2]
except IndexError:
current_char = encoded_flag[char_i:]
decoded_char = chr((int(current_char, 16) - 0x03) ^ 90)
print(decoded_char)
decoded_flag += decoded_char
print(decoded_flag)
Now let’s fill the encoded_flag variable
From the assembly we had before we can just get the full string, but there’s an important thing to take into account, not all MOVs are performed equally The second to last MOV actually overwrites some of the characters from the one done before (at 0x0040121d)
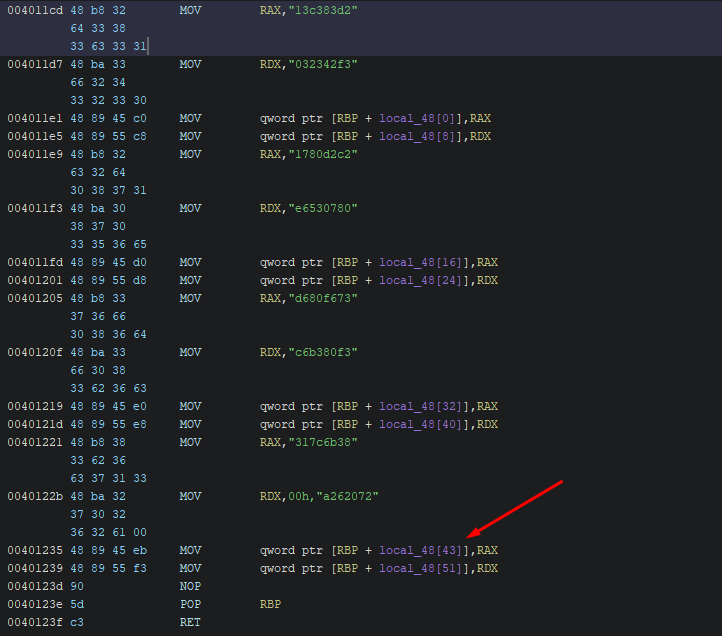
To avoid any mistake when copying or transforming the string, it’s better to do it in an automated way, so for this I will be showcasing ghidralib.
You can go read the documentation for a more in depth tutorial, but basically I will:
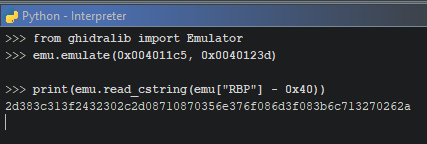
- Use the emulator to emulate the desired function from
0x004011c5to0x0040123d - get the value from the stack
so the variable that the function builds seem to be 0x48 long but values are only loaded up to RBP - 0x40.
We can put this result into our script anddddd…
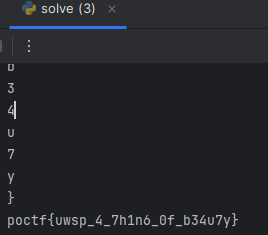
Flag
user: root: 